Renaming Files & Folders
To rename a file or folder, hit the relevant keyboard shortcut or right-click and select “Rename” to bring up the Rename dialog.
This dialog will, depending on the context, provide access to different renaming “modes”:
Regular Renaming
Regular renaming is just a basic text input that validates the input as you type.
This mode is not accessible when you have selected multiple files.
Batch Renaming
You can use the batch-renaming to quickly and easily transform the name of multiple files.
This mode is accessible when you are renaming more than one file.
Add Text
Select this mode to insert the specified text before or after the filename (but before the extension).
Replace Text
Select this mode to enter some text which should be replaced by some other piece of text (or simply be removed).
Advanced Renaming
Advanced renaming can be used to “imprint” your file names with all kinds of data. It might be the tempo of a given sound, the current time or even the name of the currently logged-in user.
To begin with, simply choose to rename one or more files. You should notice that the Rename dialog has been extended with an “advanced” mode:
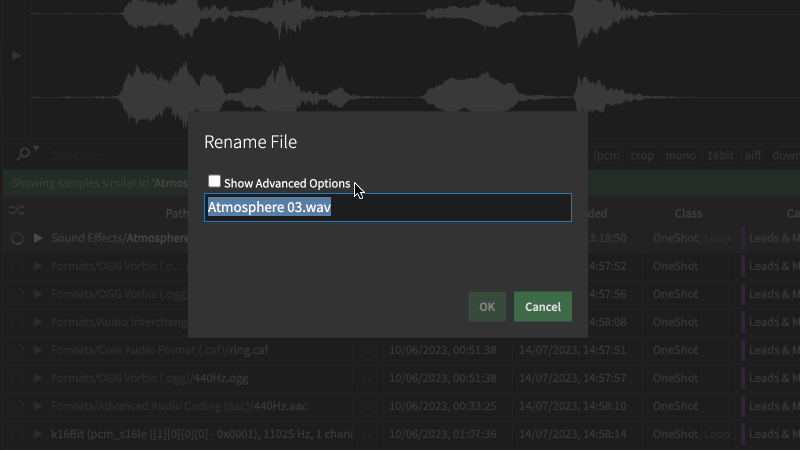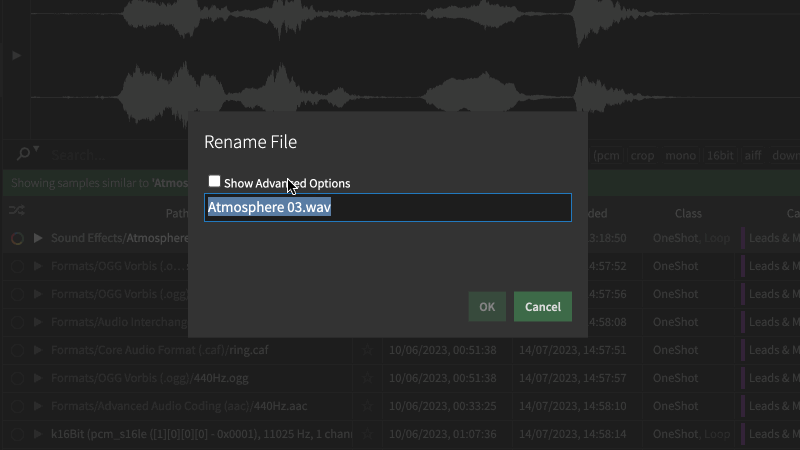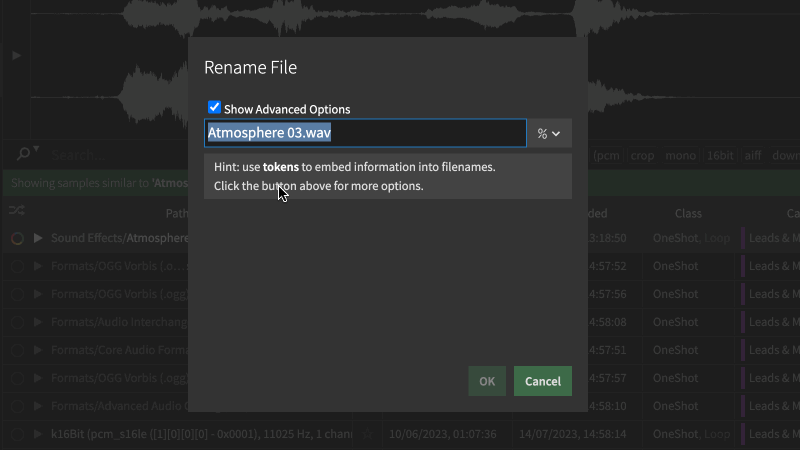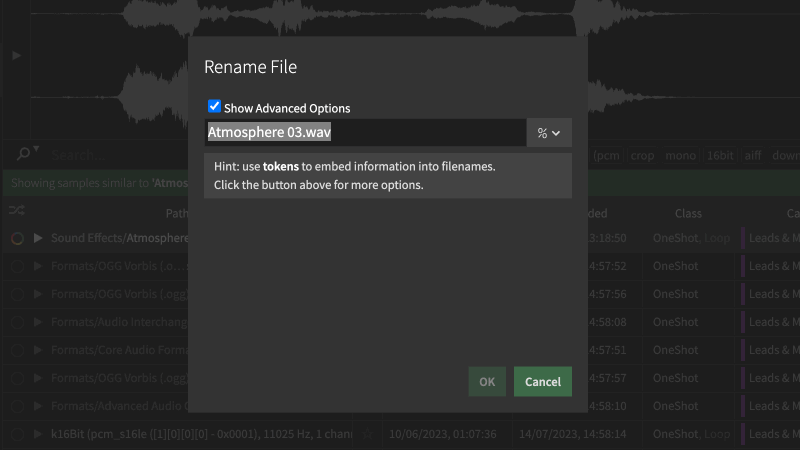
Use Tokens to fetch data
Once you enter the advanced mode, you can enter special values, so-called “tokens” into the name - each of which will embed a certain piece of information into the filename.
Tokens can also be accessed from the popout menu on the right side of the text input.

Demonstrating how to enter a token manually, or by selecting it from the popout menu.
Underneath the text input, you’ll see a preview which updates as you type, pulling information from the file and/or library. In addition, the preview will inform you when the input contains a syntax error or unknown value.
Use Modifiers to get the syntax right
You can add so-called “modifiers” to change the value of a token. For example, you might want all text to be lower-case.
Modifiers are specified by entering a colon, the name and arguments immediately after the token. And just like tokens, modifiers can also be accessed from the popout menu on the right side of the text input.
Here we define a “replace” modifier that replace any occurrence of “foo” with “bar”:
%user:replace(foo:bar)%
Modifiers can also be chained together, simply by adding another modifier following the first one. if you specify more than one modifier, they are parsed in left-to-right order.
For example, %user:wrap(before_:_after):upper()% might output BEFORE_USERNAME_AFTER, as the wrapping text got transformed into uppercase.
Token Reference
Here are the most important tokens in alphabetical order:
| Identifier | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| added | number | The time when file got added to Library/Location. |
| basenote | number | The detected pitch, expressed as a MIDI-compatible note value. |
| bits | number | The bit depth of the audio signal. |
| bpm | number | The detected BPM (beats-per-minute) of the sound. |
| brightness | number | The perceived ‘brightness’ of the sound. |
| categories | string[] | The category, or categories that were found to be the best match. |
| category | string | The primary category (shorthand for categories[0]). |
| channels | number | The number of channels present in the audio signal. |
| class | string | The primary class (shorthand for classes[0]). |
| classes | string[] | The sound class: either ONESHOT, LOOP, or a combination of both. |
| crest | number | Crest Factor describes the ratio between peak and RMS, and can indicate how ‘dense’ or ‘sparse’ a given signal is. |
| favorite | number | Whether the file has been marked as a favorite, and when (expressed as timestamp). |
| filename | string | The filename, including extension (file.wav). |
| basename | string | The filename without file extension. |
| extname | string | The file extension (e.g. ‘wav’), without a leading dot. |
| filesize | number | The size of the file, in kilobytes. |
| filetype | string | The filetype / file format (e.g. ‘wav’). |
| foldername | string | The path within the Library, relative to the selected folder. |
| harmonicity | number | The perceived ‘harmonicity’ of the sound. |
| hidden | number | Whether the file is hidden, and when it got hidden (expressed as timestamp). |
| host | string | The hostname of the computer |
| id | number | The ID of this particular sound within the library. |
| length | number | The duration of the sound, in seconds. |
| library | string | Path/name of originating Library. Useful if content has arrived from multiple different libraries. |
| modtime | number | File Modification Date (expressed as timestamp). |
| noisiness | number | The perceived ’noisiness’ of the sound. |
| nowtime | number | The current time (expressed as timestamp) |
| octave | number | The octave value of the detected pitch. |
| peak | number | The Peak amplitude in the sound, expressed as decibel (dB). |
| pitchclass | string | The pitch class of the note, e.g. ‘C’ or ‘E#’. |
| rms | number | RMS: The average amplitude expressed in decibel (dB). |
| samplerate | number | The sample rate of the audio signal. |
| seq | number | Running sequence: see detailed description below. |
| status | string | Whether the asset was succesfully analyzed - or error message, if not. |
| user | string | The name of the currently logged in user |
In addition to the tokens above, you can include metadata by specifying the name of the metadata column, prefixed with meta: (for example, meta:artist).
Modifier Reference
Use modifiers to change the input provided by a token. If you specify multiple modifiers, they will be processed in a left-to-right order. The modifiers are divided into three categories: numbers, strings and date modifiers.
Note: each modifier will expect either a number or string as input, but will automatically try to convert the input into the appropriate format.
Number Modifiers
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| abs | Returns the absolute value of a number (the value without regard to whether it is positive or negative). |
| add | Increase the value by the specied amount |
| sub | Decrease the value by the specied amount |
| mul | Multiply the value by the specied amount |
| div | Divide the value by the specied amount |
| modulo | Perform integer division and return remainder |
| range | Scale the number by providing a source and target range (4 values in total) |
| ceil | Returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to its numeric argument. |
| digits | Returns a string representing a number in fixed-point notation. |
| floor | Returns the greatest integer less than or equal to its numeric argument. |
String Modifiers
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| lower | Converts all the alphabetic characters in a string to lowercase. |
| upper | Converts all the alphabetic characters in a string to uppercase. |
| lpad | Pads the current string with a given string (possibly repeated) so that the resulting string reaches a given length. The padding is applied from the start (left) of the current string. @param maxLength: The length of the resulting string once the current string has been padded. If this parameter is smaller than the current string’s length, the current string will be returned as it is. @param maxLength: The string to pad the current string with. If this string is too long, it will be truncated and the left-most part will be applied. The default value for this parameter is " " (U+0020). |
| replace | Replaces text in a string, using a regular expression or search string. @param searchValue — A string or regular expression to search for.@param replaceValue — A string containing the text to replace. |
| rpad | Pad the current string with a given string (repeated, if needed) so that the resulting string reaches a given length. The padding is applied from the end (right) of the current string.. @param maxLength: The length of the resulting string once the current string has been padded. If this parameter is smaller than the current string’s length, the current string will be returned as it is. @param maxLength: The string to pad the current string with. If this string is too long, it will be truncated and the left-most part will be applied. The default value for this parameter is " " (U+0020). |
| wrap | Wrap the input in the provided value. If two arguments are provided, first argument is used for the left side and second for the right side. Otherwise, the first argument is used for both sides. |
Date Modifiers
These modifiers all expect a numeric unix timestamp as input (e.g. %nowtime%, %modtime%, %favorite% and %hidden%)
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| date | Output the day in two-digit format (DD) |
| month | Output the month in two-digit format (MM) |
| year2 | Output the year in two-digit format (YY) |
| year4 | Format timestamp as year, using 4 digit format (YYYY) |
Sequence
Files will automatically have a number (the “running sequence”) assigned to them when they are renamed. This makes it possible to ensure that the original order is kept.
A special case here is the Project: when some files have already added to a project, and you apply a profile which makes use of the %seq% token, the user will be prompted if the numbering should be updated:

Naming Profiles
A Naming Profile is a “template” which can be used when renaming files. Use it to define more complex, reusable patterns containing multiple tokens and/or modifiers.
To view/edit or create Naming Profiles
To view/edit/create a profile, head into the application menu > View > Show Naming Profile Editor
The application comes with a few ready-made profiles that demonstrate how the feature works. But you can also define your own profiles from scratch, or base it on an existing profile.
To apply a Naming Profile to items in a Project:
- Open the Project sidepanel.
- Select the desired items (files).
- Click the “%” symbol to bring up the dropdown menu.
- Select your desired profile.
To apply a Naming Profile to items in the Browser:
- Bring focus to the Browser (CTRL/CMD+K)
- Select the desired files.
- Right-click and choose ‘Assign Naming Profile’
- Select your desired profile.
Examples
Prefix entries with running sequence index (3 digits)
pattern:
%seq:lpad(3:0)%-%filename%
input:
Foobar.wav
Barfoo.wav
Barbaz.mp3
output
000-Foobar.wav
001-Barfoo.wav
002-Barbaz.mp3
Embed note information into filename (octave, pitch class)
pattern:
%pitchclass:rpad(-:2)%%octave%
input:
Foobar.wav
Barfoo.wav
Barbaz.mp3
output
C-1.wav
E#2.wav
F-4.mp3
Display embedded metadata (artist/album/song info)
pattern:
%meta:artist%,%meta:album%,%meta:title%
input:
file_with_embedded_metadata.mp3
output:
Depeche Mode,Memento Mori,Speak to Me.mp3